Coal Analyzer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Coal analyzers are 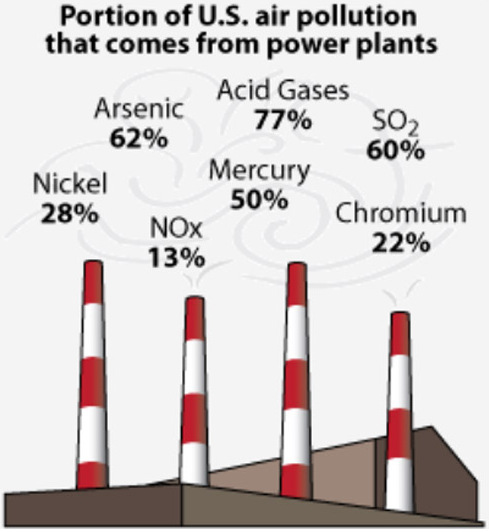 Coal quality parameters of greatest interest include ash, moisture, sulfur, and
Coal quality parameters of greatest interest include ash, moisture, sulfur, and
bulk material analyzer The term bulk material analyzer is the generic noun for that device which fits around a conveyor belt and conducts real-time elemental analysis of the material on the belt. Other names often found for such a device include ''belt analyzer'', ''cros ...
s used by coal producers, coal preparation plant
300px, A coal "washer" in Eastern Kentucky
A modern coal breaker in Mahanoy City, Pennsylvania combines washing, crushing, grading, sorting, stockpiling, and shipping in one facility built into a stockpile of anthracite coal below a mountain top ...
s, and coal-fired power plants
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
to determine coal quality in real time.
 Coal quality parameters of greatest interest include ash, moisture, sulfur, and
Coal quality parameters of greatest interest include ash, moisture, sulfur, and energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extract ...
(also known as heat content). Although most coal operations can obtain this information about coal quality by taking physical samples, preparing the samples, and analyzing them with laboratory equipment, these processes often involve a time lag of up to 24 hours from gathering the sample to final analysis results. In contrast, coal analyzers provide analysis information each minute on material being transported by conveyor either at the mine or the power plant. This timely coal quality information in turn allows the operator to improve his process by taking timely process control
An industrial process control in continuous production processes is a discipline that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. I ...
actions, such as sorting, blending, coal homogenization
Coal homogenization refers to the process of mixing coal to reduce the variance of the product supplied. This homogenization process is performed during the coal stockpiling operation. Although the terms blending and homogenization are often used ...
, or prep plant control.
There are several different types of coal analyzers. Some of the more sophisticated analyzers use prompt gamma neutron activation analysis
Prompt-gamma neutron activation analysis (PGAA) is a very widely applicable technique for determining the presence and amount of many elements simultaneously in samples ranging in size from micrograms to many grams. It is a non-destructive method, ...
(PGNAA) or pulsed fast thermal neutron activation (PFTNA) to determine the elemental content of the coal. Another emerging technology for elemental analysis is laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a type of atomic emission spectroscopy which uses a highly energetic laser pulse as the excitation source. The laser is focused to form a plasma, which atomizes and excites samples. The formation of ...
(LIBS). PGNAA and LIBS enable analysis of sulfur and ash (the latter, by summing the ash constituents). When combined with a second type of analyzer, the moisture meter
Moisture meters are used to measure the percentage of water in a given substance. This information can be used to determine if the material is ready for use, unexpectedly wet or dry, or otherwise in need of further inspection. Wood and paper prod ...
, they provide moisture and energy value as well. Moisture meters are often found in conjunction with the elemental analyzers, but sometimes are used alone, or in conjunction with ash gauges. Most moisture meters use microwave technology. The emerging technology of magnetic resonance (MR) offers a more direct measurement. Most ash gauges employ gamma attenuation principles.
Coal analyzers were first introduced in the early 1980s with the US and Australia leading the way. The demand for coal analyzers has been highest in the US, due to the need to control sulfur as mandated by the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1977. By 2005, more than 600 coal analyzers were in use throughout the world. Most of these analyzers are mounted around an existing conveyor belt, although a significant minority analyze sample streams taken from the main process stream.
References
*Davis, Vaughn, "Titan CCA - A New Type of Coal Analyzer", presented to D5 Committee of ASTM, Anaheim, California, May 17, 2011. *Snider, Kurt, "Using An On-Line Elemental Coal Analyzer to Reduce Lost Generation Due to Slagging", International On-Line Coal Analyzer Technical Conference, St. Louis, November 8–10, 2004. *Evans, Michael, "Cost Justification for a Coal Analyzer Installation", International On-Line Coal Analyzer Technical Conference, St. Louis, November 8–10, 2004. *Woodward, Richard, Eric Empey, Michael Evans, "A Major Step Forward for On-Line Coal Analysis", Coal Prep 2003 Conference, Lexington, Kentucky, April 30, 2003. {{DEFAULTSORT:Coal Analyzer Coal-fired power stations